
The Periodic Table
By the end of this lesson, the learner will be able to:
Appreciate the reason for the orderly arrangement of elements on the periodic table.
Draw the periodic table for the first 20 elements.
Efficiently arrange electrons on the shell of an atom.
Draw the electron configuration of the first 20 elements.
Understand how ions are formed.
Know the difference between elements and compounds.
Form covalent bonds between elements and compounds.

Admin
About This Course
The Periodic Table
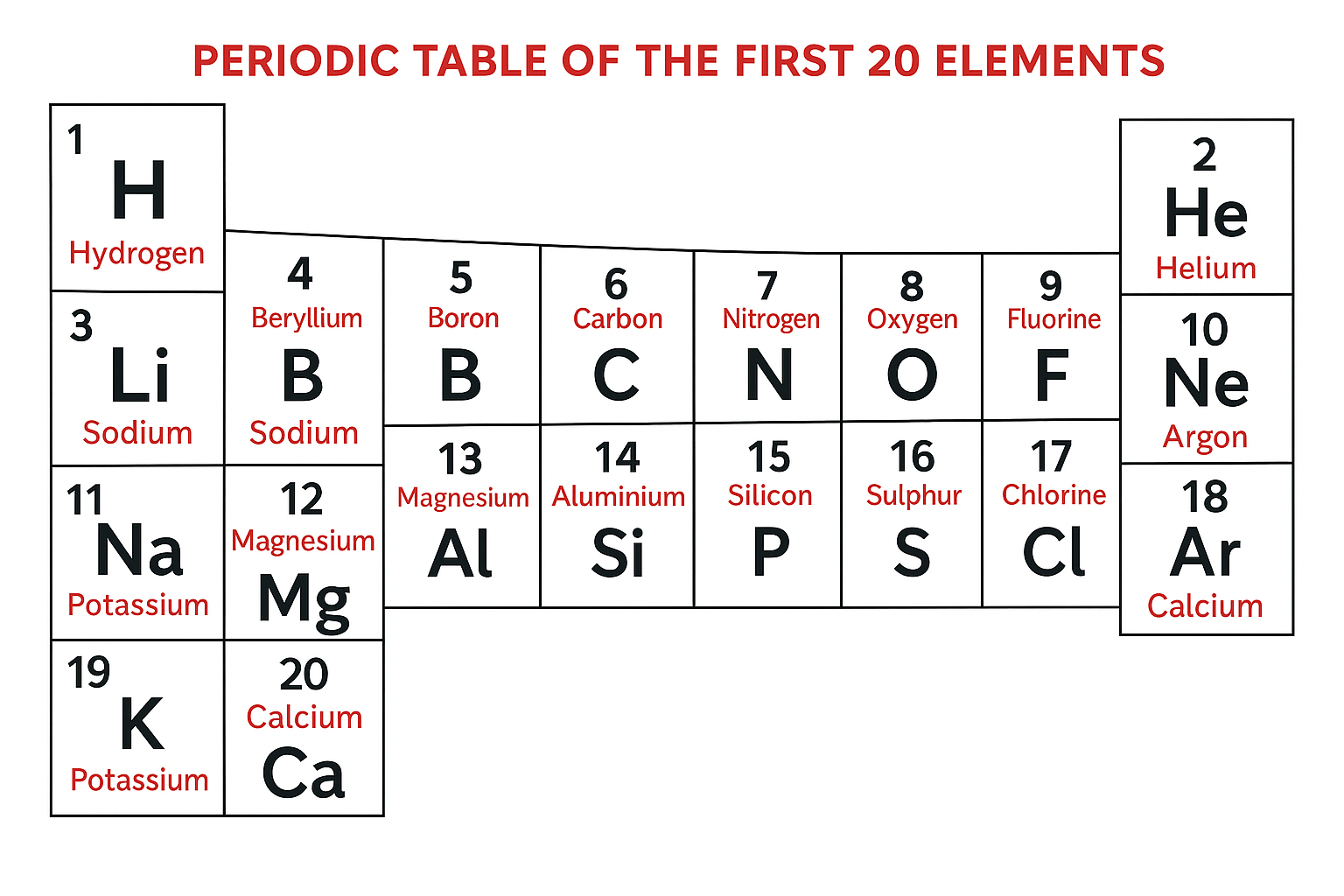
Chemical elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number.
The horizontal rows are called Periods and the vertical columns are called Groups.
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of outer electrons, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
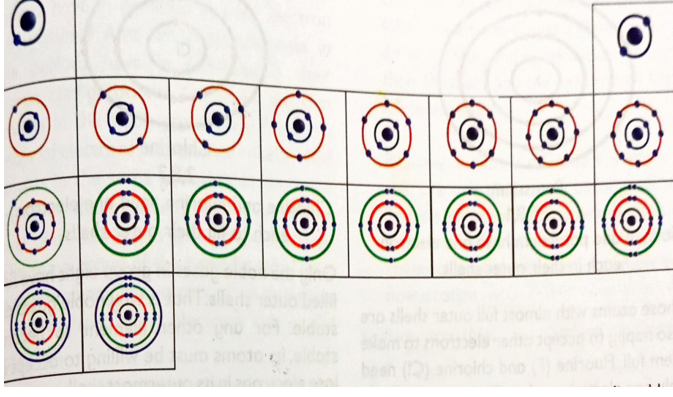
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
The arrangement and distribution of electrons in the shells
of an atom is called Electronic Configuration.
Electrons occupy shells starting with the innermost shell
and begin to occupy the next shell only when a shell becomes full.
Both circles and numbers are used to represent electron
configuration.
Electrons always fill the lowest energy level/ shells first.
Each shell has its capacity. The first shell can take a
maximum of 2 electrons , second shell 8 electrons and the third shell can also
take 8 electrons.
In most atoms, the outer shell is not full and as a result
they are unstable and want to react.
Example 1
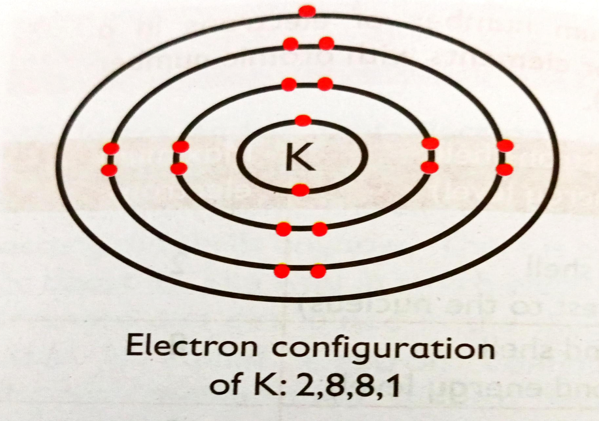
What is the electronic configuration of potassium?
Answer
The atomic number of potassium is 19. Potassium has 19
protons and 19 electrons.
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION OF THE FIRST TWENTY ELEMENTS
FORMATION OF IONS
In most atoms the outer shell is not full and this makes
them unstable and want to react. Some atoms will lose a few electrons in their
outer shells to obtain stability while others are happy to accept electrons to
be able to fill their outer shells in order to be stable.
The number of electrons an atom must lose or gain to attain
the nearest noble gas electron configuration is its VALENCY.
The noble gases are Helium, Neon and Argon.
Valency determines the ability of an atom to become an ION.
Valency is the combining power of an element to form an ion.
Example
Potassium has one electron in its outer shell, potassium is
willing to give away the only one electron in its outer shell in order to
become stable.
Chlorine has 7 electrons in its outer shell and is happy to
accept other electrons to make the shell full.
An ION is an atom or group of Atoms with a positive or negative
charge. Ions are formed when Atoms lose or gain electrons to obtain a full
outer shell resulting in a change in the number of electrons as compared to the
number of protons.
When an atom loses an electron, the number of electrons
becomes less than the number of protons. The charge on the atom becomes
positive. A positively charged ion is called CATION.
Group 1 and group 2 elements are metals and they easily
lose electrons to become positively charged Cations.
Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions
because when electrons are gained, the number of electrons becomes more than
the number of protons resulting in a negative charged ion known as an ANION.
Group 6 and 7 elements are non metals, they gain electrons
to become negatively charged ions.
COVALENT BONDING
This type of bond is formed when electrons are shared
between two atoms in which both atoms involved need to gain electrons to
achieve stability. In covalent bonding, each of the participating atoms
contributes electrons to be shared. The pair of electrons is attached to the
nuclei of both atoms forming a covalent bond.
A molecule is a combination of two or more atoms joined
together by covalent bonds.
Molecules can be a combination of same atoms or different
atoms.
Molecules of the same atoms form ELEMENTS
Molecules of different atoms form COMPOUNDS.


Curriculum Overview
This course includes 0 modules, 0 lessons, and 0 hours of materials.

Course Specifications




Reply to Comment